Hypersonic Jets
- Details
- Last Updated on Wednesday, 06 July 2016 17:18
 |
New Journal of Physics (2011): videoabstract | |
 |
The experimental setup. By means of a fast piston mounted on the left, the jet gas is compressed to stagnation pressures ranging from 0.1 to 0.7MPa, and is accelerated by a de Laval nozzle. The jet travels along a vessel filled with the desired ambient gas (at pressures in the 1.5–100 Pa range) and meets an electron sheet. The sheet ionizes the gases and makes a plane section of |
|
 |
The vessel - Jet generation at the nozzle (movie). |
|
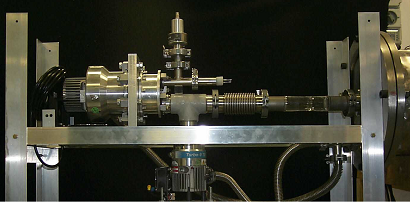 |
The electron gun | |
 |
Underexpanded jet, He/Ar (see movie) |
|
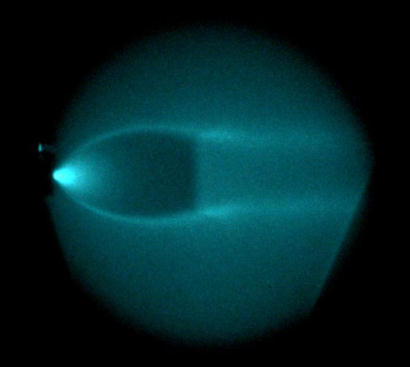 |
Underexpanded jet, Ar/He | |
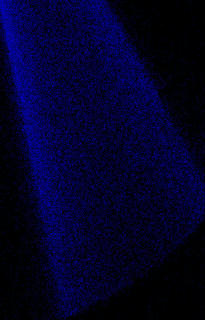 |
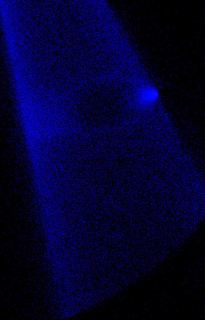 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
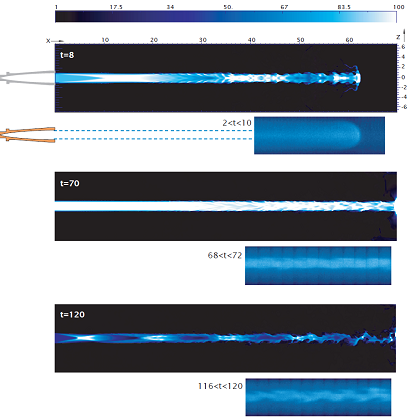
Light jet, helium in xenon, M= 16.1. Density maps: numerical simulations and experimental measurements. - movie (numerical simulation) - movie (experiment) |
|
 |
Heavy jet, Xenon in air, M= 15. Density maps: numerical simulations and experimental measurements. - movie (numerical simulation) - experimental movies (Xe in Ar): original and reworked by means of multicorrelation techniques. |
|
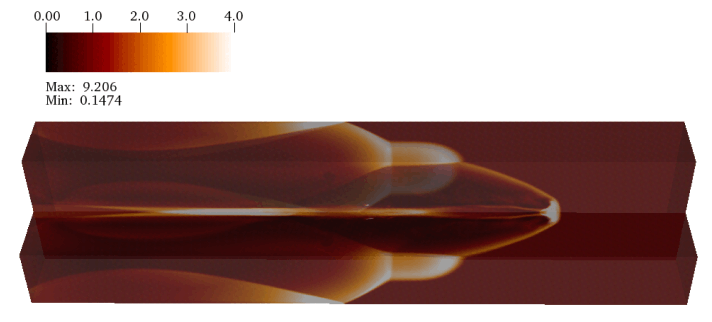 |
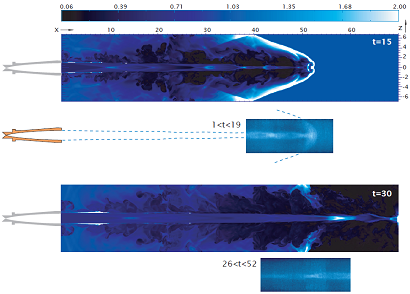
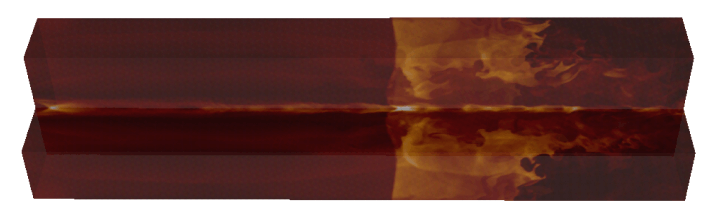
Light jet, numerical simulation.
t = 15 t_jet |
|
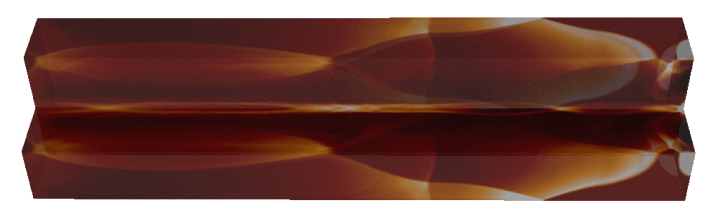 |
t = 20 t_jet |
|
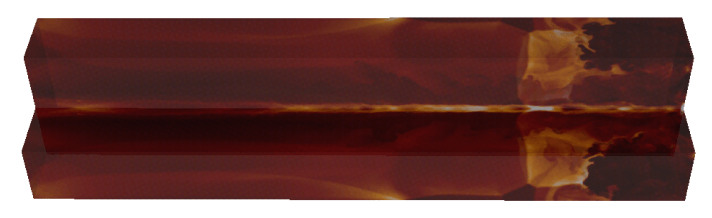 |
t = 30 t_jet |
|
 |
t = 40 t_jet |
|
 |
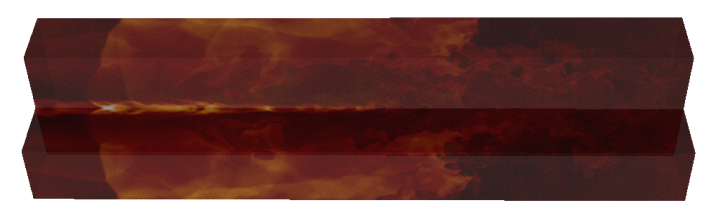
t = 50 t_jet |
|
 |
t = 60 t_jet |
| Visualizations from a large-Eddy simulations of a compressible with M=5. The simulation follows the temporal evolution of a initially round 3D jet subject to periodicity conditions along the longitudinal direction. The smagorinsky model has been used together with the selective filtering procedure. | ||
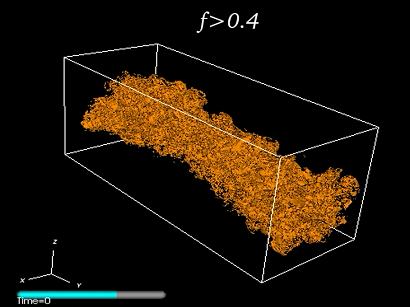 |
Large-eddy simulation of an hypersonic jet at M=5. The figure shows the underresolved regions where the small scale indicator f is larger than the threshold 0.4. For more details refer to CPC (2007) and (2013) A complete movie of this time evolving jet can be seen here. |
|
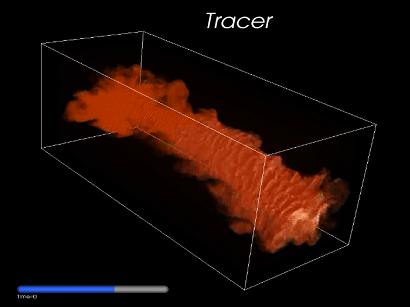 |
Large-eddy simulation of an hypersonic jet at M=5. The figure shows a passive tracer introduced at t=0 in the initially round jet. A complete movie of this time evolving jet can be seen here. For more details on the simulation refer to CPC (2007) and(2013) |
|
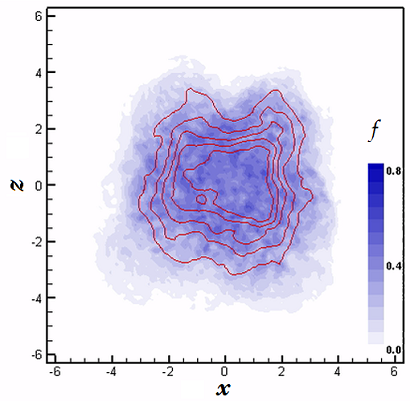 |
Large-eddy simulation of an hypersonic jet at M=5. The blue contours indicate the fraction of space where sub-filter scales are present, the red lines are the isolines of the streamwise velocity u/u0. See movie. |
|



