The cardiovascular dynamics is studied by means of lumped (0D) and multiscale (0D-1D) models. The lumped parameterization, consisting of a network of compliances, resistances, and inductances, allows to describe the complete cardiovascular system: the pumping heart together with the systemic and pulmonary circuits. The multiscale model focuses on the heart-arterial interaction. A lumped parameterization of the left heart and distal circulation is implemented, while 1D modeling of large-to-medium systemic arteries is accounted for.
The modeling resolution leads to describe the cardiovascular system in terms of the characteristic fluid dynamics variables (pressures, volumes, flow rates) and the hemodynamic parameters able to evaluate the cardiac efficiency and performance. Both models are developed and used to study cardiac pathologies, with particular attention to the cardiac arrhythmia and related altered clinical conditions.
LUMPED-PARAMETER MODELING
In the lumped parameterization the anatomical details are neglected and the whole cardiovascular system (with both systemic and pulmonary loops) is represented through the windkessel model by a set of electrical components, such as compliances, resistances and inductances.
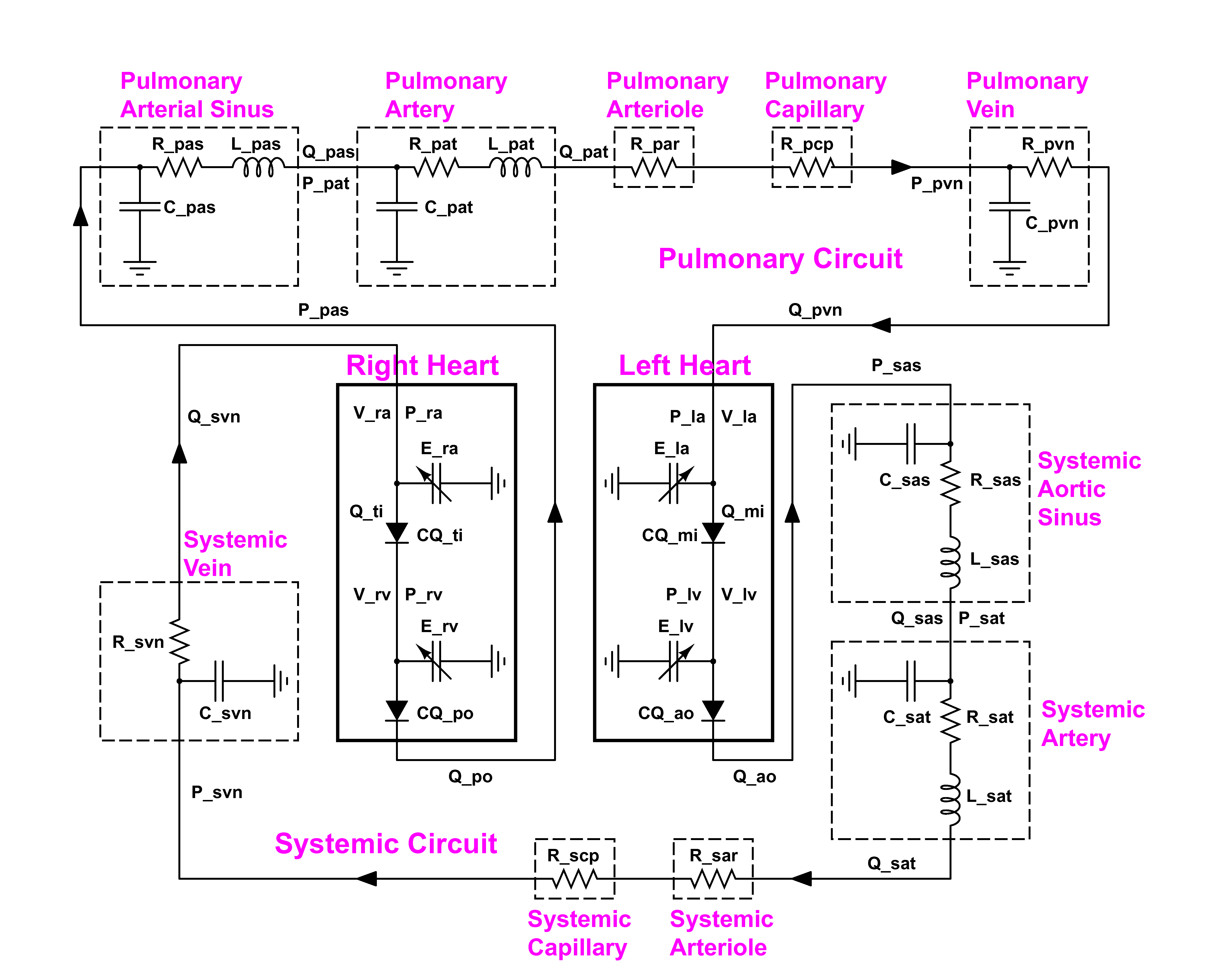
Figure 1: scheme of the cardiovascular system.
Particular attention is paid to the physiologic and fibrillated beating features: (i) the normal beating (NSR, in blue) with full atrial contractility and RR beats extracted from a Gaussian distribution, and (ii) the fibrillated beating (AF, in red), with no atrial contraction and RR beats extracted from an Exponentially Modified Gaussian distribution. Interbeat analysis is also carried out on real RR series collected in the MIT database.
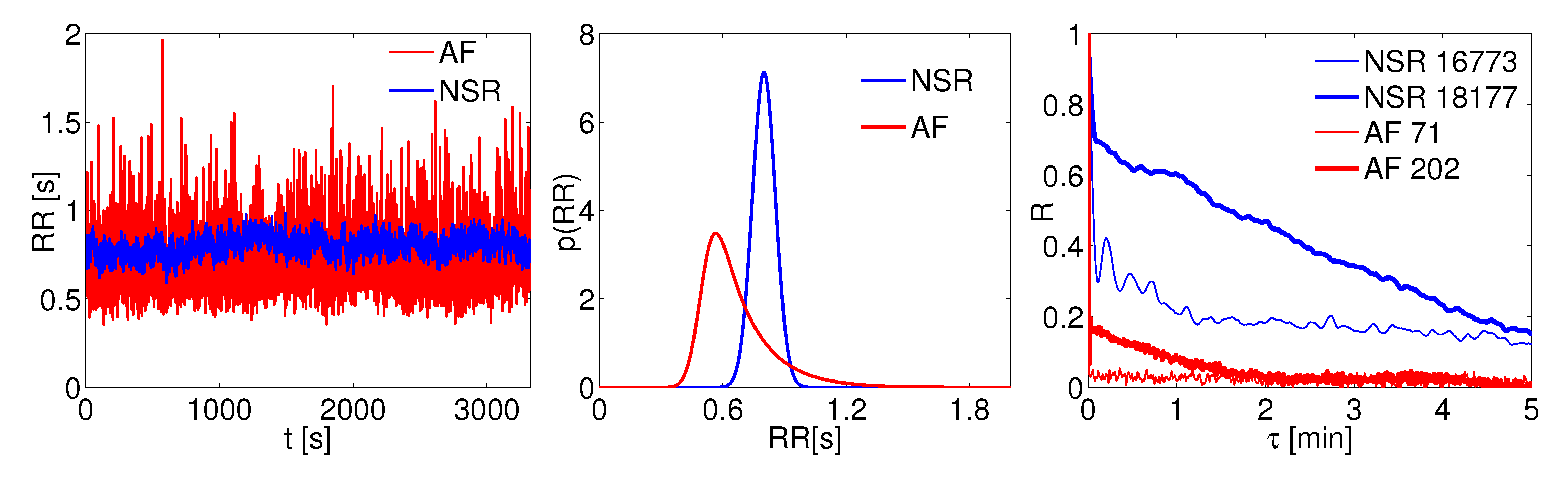
Figure 2: RR beating features. (left) RR temporal series; (middle) RR distributions; (right) autocorrelation functions, R (real RR recordings).
An overview of the main outcomes, computed over thousands of cardiac cycles and focused on the leaft heart, compares the normal sinus rhythm (NSR, in blue) and the atrial fibrillation (AF, in red). The model predictions well agree with the state-of-the-art clinical measures regarding AF: there is an overall deterioration of the hemodynamic framework with reduced cardiac efficiency and performance. The present stochastic modeling turns out to be an efficient and powerful tool for a deeper comprehension of the arrhythmia impact on the whole cardiovascular system.
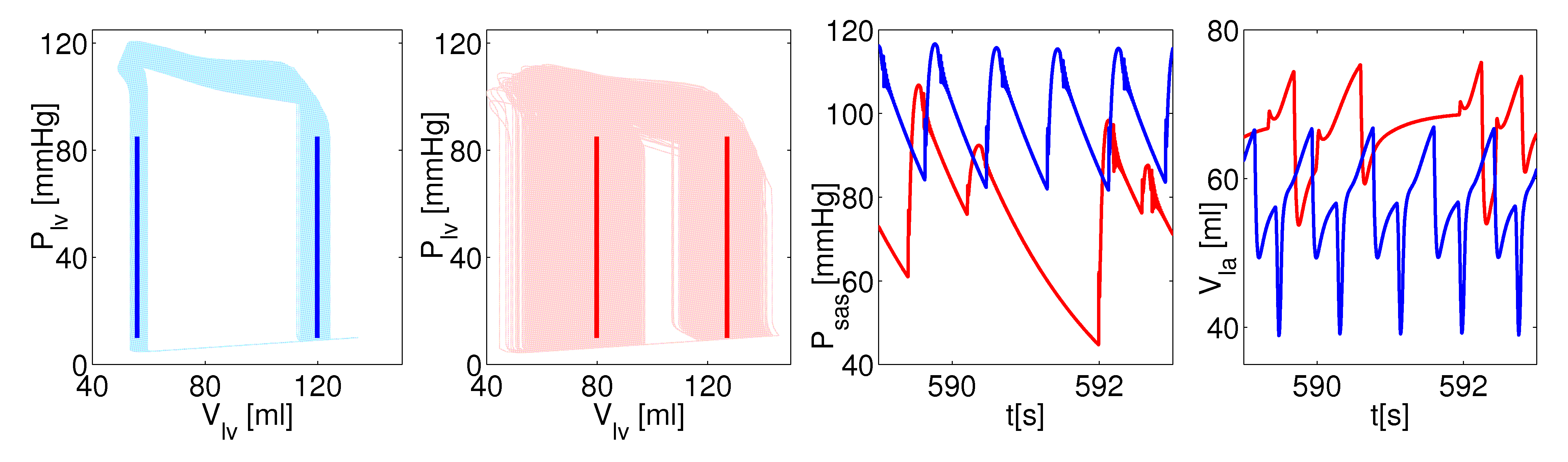
Figure 3: left heart dynamics. From left to right: PV loops during NSR; PV loops during AF; systemic arterial pressure series; left atrial volume series.
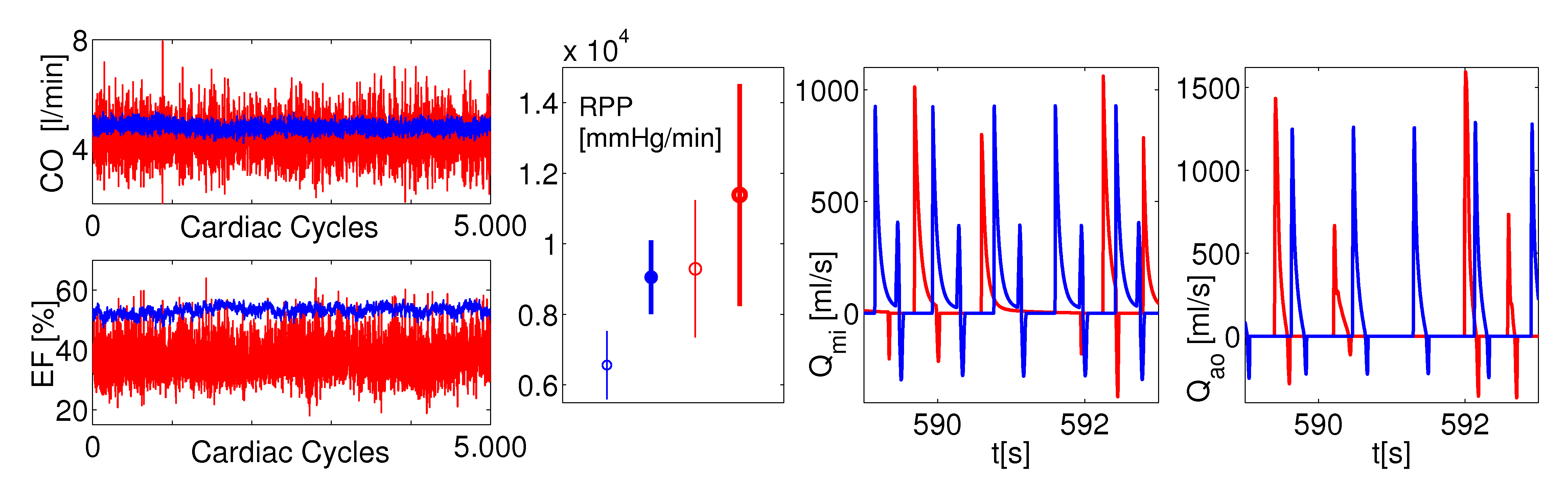
Figure 4: LV performance and flow rates. From left to right: cardiac output (CO) and ejection fraction (EF) series; rate pressure product (RPP) values averaged over 10000 cardiac cycles (RR from real recordings); mitral flow rate (Qmi) temporal series; aortic flow rate (Qao) temporal series.
MULTISCALE MODEL
With a stochastic modeling of the RR beating similar to the one used in the lumped parameterization, the multiscale model focuses on the effects of AF on the cerebral and aortic circulation. Preliminary results along the aortic tree are shown.

Figure 5: pressure time series along the aorta. (top) aortic arch; (middle) descending aorta; (bottom) abdominal aorta.
Related Publications
- F. Tripoli, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, Short-term response of cerebrovascular and ocular hemodynamics from micro- to hyper-gravity: A multiscale mathematical analysis, Acta Astronautica, 237, 159-173, 2025. [PDF]
- F. Tripoli, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, Assessing the cardiac function from micro-gravity to hyper-gravity conditions through a validated multiscale modelling approach, The Journal of Physiology, doi: 10.1113/JP287142, 2025. [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, L. Congiu, L. Ridolfi, Investigating the impact of atrial fibrillation on the vascular onset of glaucoma via multiscale cardiovascular modeling, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 267, 108783, (2025). [PDF]
- K. Calò, A. Guala, V. Mazzi, M. Lodi Rizzini, L. Dux-Santoy, J. Rodriguez Palomares, S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, D. Gallo, U. Morbiducci, Pathophysiology of the ascending aorta: Impact of dilation and valve phenotype on large-scale blood flow coherence detected by 4D flow MRI, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 255, 108369, (2024). [PDF]
- A. Saglietto, F. Tripoli, J. J. M. Zwanenburg, G. J. Biessels, G. M. De Ferrari, M. Anselmino, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, Role of the vessel morphology on the lenticulostriate arteries hemodynamics during atrial fibrillation: A CFD-based multivariate regression analysis, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 254, 108303, (2024). [PDF]
- V. N. Bhargav, N. Francescato, H. Mettelsiefen, A. Y. Usmani, S. Scarsoglio, V. Raghav, Spatio-temporal relationship between three-dimensional deformations of a collapsible tube and the downstream flowfield, Journal of Fluids and Structures, 127, 104122, (2024). [PDF]
- D. Canova, S. Roatta, A. Saglietto, S. Scarsoglio, N. R. Gianotto, A. Piccotti, G. M. De Ferrari, L. Ridolfi, M. Anselmino, A quantitative assessment of cerebral hemodynamic perturbations associated with long R-R intervals in atrial fibrillation: A pilot-case-based experience, Medicina, 60(4), 531, (2024). [PDF]
- M. Fois, A. Diaz-Artiles, S. Y. Zaman, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, Linking cerebral hemodynamics and ocular microgravity-induced alterations through an in silico-in vivo head-down tilt framework, npj Microgravity, 10, 22 (2024). [PDF]
- A. Saglietto, S. Scarsoglio, F. Tripoli, J. J. M. Zwanenburg, G. J. Biessels, G. M. De Ferrari, L. Ridolfi, M. Anselmino, Atrial fibrillation hemodynamic effects on lenticulostriate arteries identified at 7-Tesla cerebral MRI, Clinical and Translational Medicine, 13: e1367 (2023). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, M. Fois, L. Ridolfi, Increased hemodynamic pulsatility in the cerebral microcirculation during parabolic flight-induced microgravity: A computational investigation, Acta Astronautica, 211, 344–352 (2023). [PDF]
- A. Saglietto, S. Scarsoglio, D. Canova, G. M. De Ferrari, L. Ridolfi, M. Anselmino, Beat-to-beat finger photoplethysmography in atrial fibrillation patients undergoing electrical cardioversion, Scientific Reports, 13, 6751 (2023). [PDF]
- K. Calò, D. Gallo, A. Guala, A. M. Lodi Rizzini, L. Dux-Santoy, J. Rodriguez Palomares, S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, U. Morbiducci, Network-Based Characterization of Blood Large-Scale Coherent Motion in the Healthy Human Aorta with 4D Flow MRI, Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 70(3), 1095–1104, (2023). [PDF]
- M. Fois, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, Arterial wave dynamics preservation upon orthostatic stress: a modelling perspective, Royal Society Open Science, 10(3), 221257 (2023). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, A. Saglietto, F. Tripoli, J. J. M. Zwanenburg, G. J. Biessels, G. M. De Ferrari, M. Anselmino, L. Ridolfi, Cerebral hemodynamics during atrial fibrillation: Computational fluid dynamics analysis of lenticulostriate arteries using 7 T high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging, Physics of Fluids, 34(12), 121909 (2022). [PDF]
- M. Anselmino, S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, G. M. De Ferrari, A. Saglietto, Insights from computational modeling on the potential hemodynamic effects of sinus rhythm versus atrial fibrillation, Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 9: 844275, (2022). [PDF]
- M. Fois, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, In silico study of the posture-dependent cardiovascular performance during parabolic flights, Acta Astronautica, 200: 435-447, (2022). [PDF]
- M. Fois, S. V. Maule, M. Giudici, M. Valente, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, Cardiovascular Response to Posture Changes: Multiscale Modeling and in vivo Validation During Head-Up Tilt, Frontiers in Physiology, 13: 826989, (2022). [PDF]
- A. Saglietto, M. Fois, L. Ridolfi, G. M. De Ferrari, M. Anselmino, S. Scarsoglio, A computational analysis of atrial fibrillation effects on coronary perfusion across the different myocardial layers, Scientific Reports, 12(1), 841, (2022). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, A review of multiscale 0D-1D computational modeling of coronary circulation with applications to cardiac arrhythmias, Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine, 22(4): 1461-1469, (2021). [PDF]
- K. Calò, D. Gallo, A. Guala, J. Rodriguez Palomares, S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, U. Morbiducci, Combining 4D Flow MRI and Complex Networks Theory to Characterize the Hemodynamic Heterogeneity in Dilated and Non-dilated Human Ascending Aortas, Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 49(9): 2441–2453, (2021). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, Different impact of heart rate variability in the deep cerebral and central hemodynamics at rest: an in silico investigation, Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15, 600574, (2021). [PDF]
- A. Saglietto, S. Scarsoglio, D. Canova, S. Roatta, N. Gianotto, A. Piccotti, S. Franzin, F. Gaita, G. M. De Ferrari, L. Ridolfi, M. Anselmino, Increased beat-to-beat variability of cerebral microcirculatory perfusion during atrial fibrillation: a near-infrared spectroscopy study, EP Europace, 23(8): 1219–1226, (2021). [PDF]
- A. Saglietto, S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, D. Canova, M. Anselmino, Cerebral spatially resolved near-infrared spectroscopy (SRS-NIRS): paving the way for non-invasive assessment of cerebral hemodynamics during atrial fibrillation, Minerva Cardioangiologica, 69(2): 124-126, (2021) [PDF]
- C. Gallo, J. Olbers, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, N. Witt, Testing a Patient-Specific In-Silico Model to Noninvasively Estimate Central Blood Pressure, Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology, 12(2): 144-157, (2021). [PDF]
- C. Gallo, L. Ridolfi, S. Scarsoglio, Cardiovascular deconditioning during long-term spaceflight through multiscale modeling, njp Microgravity, 6(1): 27, (2020). [PDF]
- K. Calò, G. De Nisco, D. Gallo, C. Chiastra, A. Hoogendoorn, D.A. Steinman, S. Scarsoglio, J.J. Wentzel, U. Morbiducci, Exploring wall shear stress spatiotemporal heterogeneity in coronary arteries combining correlation-based analysis and complex networks with computational hemodynamics, Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine, 234(11): 1209-1222, (2020) [PDF]
- K. Caló, D. Gallo, D. A. Steinman, V. Mazzi, S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, U. Morbiducci, Spatiotemporal hemodynamic complexity in carotid arteries: an integrated computational hemodynamics & complex networks-based approach, Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 67(7): 1841–1853, (2020) [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, C. Gallo, A. Saglietto, L. Ridolfi, M. Anselmino, Impaired coronary blood flow at higher heart rates during atrial fibrillation: investigation via multiscale modelling, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 175: 95-102, (2019). [PDF]
- A. Saglietto, S. Scarsoglio, L. Ridolfi, F. Gaita, M. Anselmino, Higher ventricular rate during atrial fibrillation relates to increased cerebral hypoperfusions and hypertensive events, Scientific Reports, 9, 3779, (2019). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, C. Gallo, L. Ridolfi, Effects of atrial fibrillation on the arterial fluid dynamics: a modelling perspective, Meccanica, 53 (13), 3251–3267, (2018). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, A. Saglietto, M. Anselmino, F. Gaita, L. Ridolfi, Alteration of cerebrovascular haemodynamic patterns due to atrial fibrillation: an in silico investigation, Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 14(129), 20170180, (2017). [PDF]
- M. Anselmino, S. Scarsoglio, A. Saglietto, F. Gaita, L. Ridolfi, A computational study on the relation between resting heart rate and atrial fibrillation hemodynamics under exercise, PLoS ONE, 12(1), e0169967, (2017). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, A. Saglietto, F. Gaita, L. Ridolfi, M. Anselmino, Computational fluid dynamics modelling of left valvular heart diseases during atrial fibrillation, PeerJ, 4, e2240, (2016). [PDF]
- M. Anselmino, S. Scarsoglio, A. Saglietto, F. Gaita, L. Ridolfi, Transient cerebral hypoperfusion and hypertensive events during atrial fibrillation: a plausible mechanism for cognitive impairment, Scientific Reports, 6, 28635, (2016). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, C. Camporeale, A. Guala, L. Ridolfi, Fluid dynamics of heart valves during atrial fibrillation: a lumped parameter-based approach, Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 19(10), 1060-1068, (2016). [PDF]
- M. Anselmino, S. Scarsoglio, C. Camporeale, A. Saglietto, F. Gaita, L. Ridolfi, Rate control management of atrial fibrillation: may a mathematical model suggest an ideal heart rate?, PLoS ONE, 10(3), e0119868, (2015). [PDF]
- S. Scarsoglio, A. Guala, C. Camporeale, L. Ridolfi, Impact of atrial fibrillation on the cardiovascular system through a lumped parameter approach, Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, 52 (11), 905-920, (2014). [PDF]
